The main objects of carding are
To unwind and open the lap into very small tufts.
To extract the motes, seed bits (vegetable impurities) and. all other trash particles from the cotton.
To card the fibres which means to open the cotton, even to the separation of one fibre from all the other ( fibre to fibre separation)
To condense the fibres into sliver form
To deposit the sliver in the can
Working of revolving flat card.
Lap is placed upon the wooden lap roller. Lap roller rotates at slow speed and lap is unwound by the friction of lap roller.
Sheet of cotton now passes over the feed plate & pass under the feed roller, which is heavily loaded to grip the cotton. Feed roller feed the cotton sheet to the auction of fast revolving licker-in.
Grooved surface of the lickerin is clothed with saw tooth wire.
Lap is now well opened into very small tufts by the beating action of fast revolving licker in.
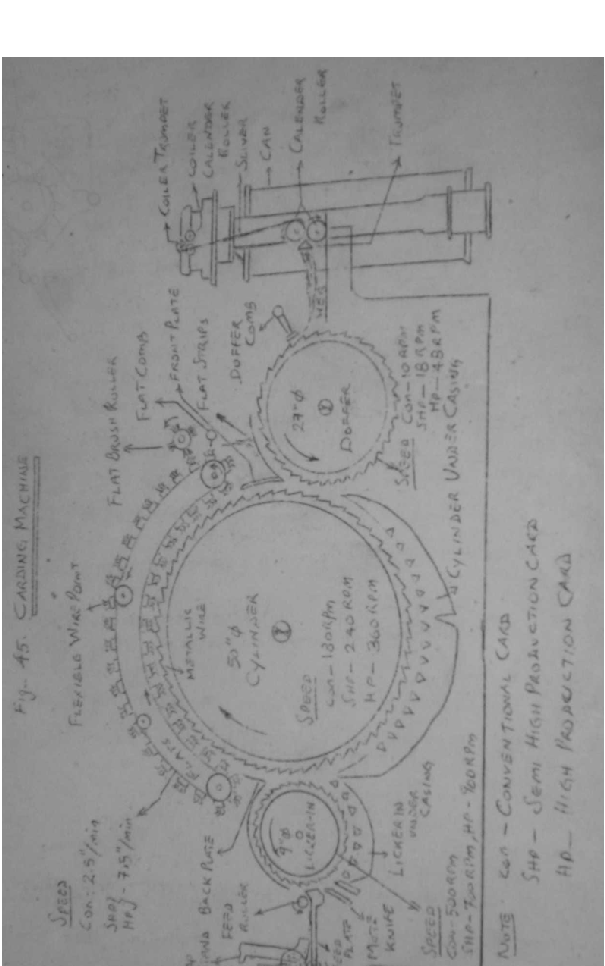
The opened fibre tufts are carried by lickerin against mote knife and over the undergrid.
Mote is a particle of seed, leaf, boll, shale or stem. Due to the resistance Of the mote knives heavily vegetable impurities known as "Mote and sand are removed and falls down through lickerin under casing.
From lickerin, the fibres are stripped off by the cylinder and carried forward to the chain of flats (app.110 flats)
Cylinder is clothed with metallic wires and flats are
clothed with flexible wires.
The wire points of flats oppose the direction of the cylinder wire points, i.e., point vs point wire sysem is placed between cylinder and flat and also, flats rotates in the same direction of cylinder, because of these reasons, carding action takes place between flat and cylinder which means fibre to fibre separation is achieved.
From cylinder, the carded fibres are transferred to the doffer surface, which is also clothed with metallic wire.
Oscillating doffer comb operating close to the doffer removes the fibres from doffer in the form of thin sheet called Web is gathered together by passing through trumpet to produce sliver, which is then compressed by a pair of calender roller.
In coiler head, the sliver is again compressed by the coiler calender Roller. Then the sliver is deposited in the form of coils in the can by the coiler mechanism, speed particulars:
(conventional card) Licker-in(9inch dia)=500 RPM
Cylinder ( 50 inch dia)=180 RPM Doffer (27 Inch dia) = 7 to 10 RPM